SBI Q2 Results: Net Profit Soars 28% to ₹18,331 Crore, Surpassing Market Forecasts
Company Overview
State Bank of India (SBI), incorporated on July 1, 1955, emerged following the nationalization of the Imperial Bank of India, with the Reserve Bank of India acquiring a 60% stake. SBI is a leading Indian multinational bank, headquartered in Mumbai, offering a broad array of financial services to individual, corporate, and institutional clients. Its extensive network is structured into four primary segments: Treasury, Corporate/Wholesale Banking, Retail Banking, and Other Banking Business. Through these, SBI provides personal banking, investment portfolios, and corporate banking services.
SBI operates one of the largest banking networks in India, with over 22,000 branches and a substantial overseas presence with 227 offices across 30 countries. Its international operations support global financial transactions from key cities like New York, Tokyo, and London. SBI also led in online initiatives, including SBI e-tax for digital tax payments, and expanded its digital footprint with innovative offerings like the SBI Virtual Debit Card for enhanced online security.
Through the years, SBI has grown through the acquisition and merger of associate banks and partnerships. Notably, in 2017, SBI absorbed five associate banks and the Bharatiya Mahila Bank, making it one of the largest global banking networks. Internationally, SBI has established joint ventures, such as the Payments Bank with Reliance Industries and collaborations with Visa and Elavon for merchant acquiring businesses.
In addition, SBI’s insurance arm, SBI Life Insurance Company, is a joint venture with Cardif S.A., and its asset management subsidiary, SBI Funds, earned the title of ‘Mutual Fund of the Year’. Domestically, SBI supports government initiatives with specialized products like the Defence Salary Package and loans for senior citizens. Its technology-driven offerings serve to enhance customer experience across both urban and rural areas.
Industry Outlook
Based on the recent financial results and statements from the chairman of State Bank of India (SBI), the industry outlook for FY25 and beyond appears positive, with several key factors contributing to growth and stability. Global growth is expected to remain stable, with the US economy showing a positive outlook, which may lead to lower taxes and favorable regulations that could benefit the Indian economy, particularly in manufacturing and strategic alliances. Additionally, a positive shift in the geopolitical situation could help lower commodity prices, benefiting India and other economies globally. India continues to be the fastest-growing large economy, with a 6.7% GDP growth in Q1 FY25, supported by private consumption, investment, and agriculture, as well as strong demand expected during the festival season.
For the banking sector, scheduled commercial banks, including SBI, are expected to see deposit growth of 11-12% and credit growth of 12-13% in FY25, with a positive deposit credit differential, which signals a healthy banking environment. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is maintaining comfortable system liquidity, which is helping support stable credit growth in the sector.
SBI itself has crossed a significant milestone, with deposits reaching ₹51.17 trillion, reflecting steady growth in its CASA deposits, which remains a strong aspect of the bank’s financial performance. Credit growth for SBI is up by 14.93% year-on-year, driven by strong performance across corporate, retail, agriculture, and MSME sectors, positioning the bank for continued market leadership. Its asset quality remains strong, with a slippage ratio of 0.51% and a PCR of 75.6%, ensuring a well-provided loan book. The bank’s capital adequacy ratio is at a solid 13.76%, well above regulatory requirements, indicating sufficient capital to support growth.
SBI’s digital transformation is another key driver of its future growth. With over 8 crore customers on its digital platforms, the bank continues to innovate in digital banking, with 61% of regular savings accounts opened digitally in Q2 FY25. The bank is focused on expanding its digital channels and strengthening its branch networks to maintain its competitive edge in the market. Furthermore, SBI’s subsidiaries, including SBI Life Insurance and SBI Funds, continue to perform well and contribute significantly to the bank’s diversified revenue streams, ensuring long-term growth.
In conclusion, SBI’s strong financial performance, particularly in credit growth, robust deposits, and its focus on digital banking, positions the bank well to benefit from the positive outlook of the Indian economy and the overall banking sector. The bank’s commitment to sustainable growth and delivering superior shareholder value over the long term remains central to its strategic priorities.
Business Segments
State Bank of India (SBI) operates across several key business segments, each contributing significantly to the bank’s overall performance. Based on the Q2 FY25 results, here’s an analysis of these segments:
- Treasury: This segment manages the bank’s investments and foreign exchange risks, as well as its bond holdings and market-based activities. The Q2 FY25 performance indicates favorable market conditions, contributing positively to the bank’s financial performance.
- Corporate/Wholesale Banking: This segment serves large corporate and government clients, offering services like working capital finance and trade finance. In Q2 FY25, corporate advances saw an impressive 18.35% year-on-year growth, contributing to an overall credit growth of 14.93%. This indicates robust demand from the corporate sector.
- Retail Banking: Serving individual customers, this segment focuses on products like personal loans, home loans, and savings accounts. The retail banking segment grew by 12.32% year-on-year in Q2 FY25, driven by demand for affordable housing and personal finance, supported by SBI’s extensive digital and physical network.
- Other Banking Business: This includes wealth management, insurance, and asset management services. Subsidiaries like SBI Life Insurance and SBI Funds Management continue to perform well, contributing non-interest income and diversifying the bank’s revenue streams.
- International Operations: SBI’s international segment, which covers over 30 countries, contributes through remittances, trade finance, and cross-border services. This segment grew by 11.56% year-on-year in Q2 FY25, reflecting the bank’s strong global presence.
SBI’s diversified operations across these segments, along with its focus on digital banking and strong capital base, position it well for continued leadership in the Indian banking sector.
Key Subsidiaries and Their Information
State Bank of India (SBI) has a diverse portfolio of subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates that contribute significantly to its operations and financial performance. Below is an overview of some of the key subsidiaries and joint ventures, along with their insights:
- SBI Life Insurance Company Ltd: As one of India’s largest private life insurance companies, SBI Life offers a broad range of products, including individual and group life insurance, pension plans, and health insurance. It continues to experience strong growth and holds a significant market share in the Indian life insurance industry. The company benefits from SBI’s vast customer base and extensive distribution network.
- SBI General Insurance Company Ltd: This subsidiary focuses on general insurance, providing products like health, motor, travel, and home insurance. SBI General is rapidly expanding its reach across India, leveraging the bank’s nationwide distribution network to increase market penetration and cater to a broader customer base.
- SBI Cards and Payment Services Limited: A leading player in the Indian credit card market, SBI Cards issues a wide range of cards catering to different customer segments. It continues to innovate in the digital payments space and has a strong presence in the Indian payments’ ecosystem, contributing to the broader digitalization trends in banking and finance.
- SBI Capital Markets Ltd (SBICAP): As the investment banking arm of SBI, SBICAP offers services such as corporate advisory, capital markets, and investment banking. It is particularly known for its expertise in handling large IPOs, mergers and acquisitions, and other capital market activities, making it an important player in India’s financial services sector.
- SBI Funds Management Ltd: SBI Funds is a major player in India’s mutual fund industry, managing a variety of mutual fund schemes for both retail and institutional clients. With its strong investment capabilities and a wide array of offerings, it plays a pivotal role in helping investors manage their portfolios.
- SBI Payments Services Pvt Ltd: This subsidiary is instrumental in expanding SBI’s footprint in the digital payments landscape. It provides innovative payment solutions, including point-of-sale (POS) terminals, digital wallets, and online payment services, contributing to the bank’s leadership in India’s digital banking sector.
- SBI Global Factors Ltd: SBI Global Factors offers factoring services primarily to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), helping them improve their liquidity by allowing them to sell their receivables. This service is especially valuable for SMEs seeking to manage cash flow more effectively.
- SBI Ventures Ltd: Formerly known as SBICAP Ventures, SBI Ventures focuses on investments in growth-stage companies, particularly in emerging sectors like technology and healthcare. Its venture capital activities align with SBI’s broader strategy to diversify beyond traditional banking and explore high-growth industries.
- State Bank of India (UK) Limited: SBI UK provides a range of retail and corporate banking services in the UK. It supports the bank’s international growth by catering to both individual customers and businesses, particularly those with ties to India, enhancing SBI’s presence in the international banking sector.
- SBI (Mauritius) Ltd: This subsidiary focuses on providing banking services in Mauritius, which acts as a gateway for SBI’s expansion into Africa. By offering a variety of financial services, SBI (Mauritius) plays an important role in strengthening the bank’s international portfolio and capitalizing on opportunities in the African market.
Each of these subsidiaries plays a key role in diversifying SBI’s business operations and bolstering its presence across multiple sectors such as insurance, payments, investment banking, and asset management. This diverse portfolio allows SBI to maintain its leadership in the Indian banking sector while also expanding globally.
Key Joint Ventures of SBI
- SBI Macquarie Infrastructure Management Pvt. Ltd: A joint venture between SBI and Macquarie Group, this entity focuses on managing infrastructure investments in India, particularly in areas like roads, power, and utilities.
- SBI Macquarie Infrastructure Trustee Pvt. Ltd: This joint venture manages infrastructure investment trusts, which help in raising capital for infrastructure projects across India.
- Jio Payments Bank Ltd: A partnership between SBI and Reliance Jio, Jio Payments Bank aims to offer digital payment solutions and banking services to customers, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Oman India Joint Investment Fund – Management Co Pvt. Ltd: This JV focuses on managing investments in India, especially in sectors that attract foreign investments.
Key Associates of SBI
- Andhra Pradesh Grameen Vikas Bank: This associate focuses on providing banking services to rural populations in Andhra Pradesh, particularly to promote financial inclusion.
- Nepal SBI Bank Ltd: This associate operates in Nepal, providing a range of banking services to the growing market there.
- Commercial Indo Bank LLC, Moscow: This associate bank serves Indian expatriates and businesses in Russia, helping them with banking and financial services.
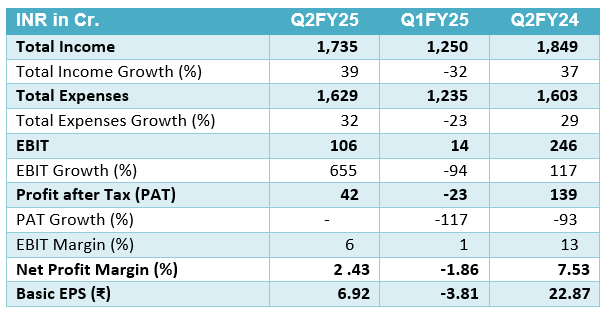
Q2 FY25 Highlights
- This Q2FY25 data indicates a solid performance with key highlights across profitability, business growth, asset quality, and digital leadership.
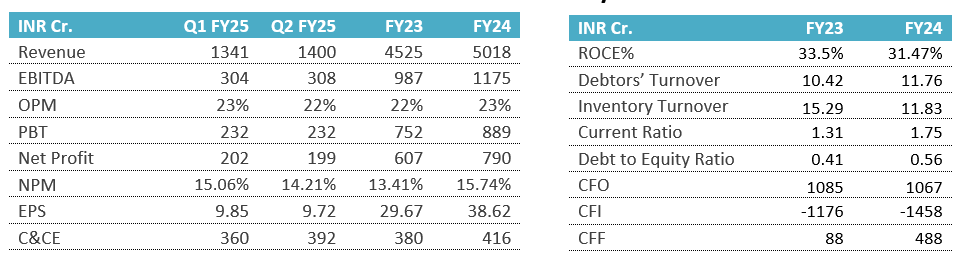
- Profitability: The bank reported a Net Profit of ₹18,331 crores in Q2FY25, showing robust earnings. Return on Assets (ROA) was at 1.13% for H1FY25, and Return on Equity (ROE) was 21.78%, reflecting efficient use of equity capital. The Net Interest Margin (NIM) was 3.18% for the whole bank and slightly higher in domestic operations at 3.31%, which supports sustainable profitability.
- Business Growth: The bank’s deposits crossed the ₹51 trillion mark, growing 9.13% YoY, while advances exceeded ₹39 trillion, with a strong 14.93% YoY growth in credit. This broad-based growth demonstrates expansion in both deposits and credit across market segments, positioning the bank for continued market share growth in a competitive environment.
- Asset Quality: Improvements in asset quality are evident, with Gross NPA at 2.13% and Net NPA at 0.53%, reflecting strong risk management. The credit cost for H1FY25 was 0.43%, indicating reduced provisioning needs due to improved loan quality. The Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR) stands at 75.66%, and including AUCA (Accounts Under Collection Account), it reaches 92.21%, demonstrating conservative provisioning for stressed assets.
- Well-Provided Stressed Book: Additional provisions of ₹31,084 crores are set aside, equating to 153% of Net NPAs, which adds a layer of resilience and minimizes potential future losses from non-performing assets.
- Digital Leadership: Digital transformation is leading growth, with >98% of transactions occurring through alternate channels. The bank’s mobile app, YONO, has 8.13 crore registered users, reinforcing its digital-first strategy. Notably, 61% of savings accounts were opened via YONO in Q2FY25, underscoring its impact on customer acquisition and engagement.
- The bank’s liability franchise benefits from brand trust and market share dominance (~22% in deposits), with a 10.05% YoY growth in current account balances. Its credit-to-deposit ratio at 67.87% indicates a healthy balance between deposit inflows and lending activities.
- The Central Board has approved raising up to ₹20,000 crore in long-term bonds during FY25. These funds may be raised via public issue or private placement, providing the flexibility to select the best approach based on market conditions. The initiative aims to enhance the bank’s capital base, supporting business growth, credit expansion, and financial resilience. This capital boost aligns with the bank’s strategic goals of strengthening its capital structure and sustaining a healthy credit-to-deposit ratio for stable, long-term growth.
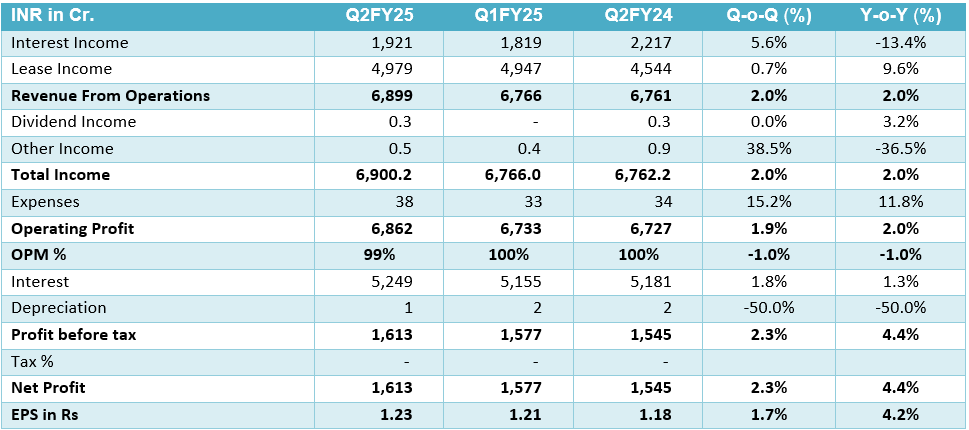
Financial Summary (Standalone)
| Type | Q2FY25 | Q1FY25 | Q2FY24 | Q-o-Q (%) | Y-o-Y (%) |
| Interest Income | 1,13,871 | 1,11,526 | 1,01,379 | 2.1% | 12.3% |
| Interest Expenses | 72,251 | 70,401 | 61,879 | 2.6% | 16.8% |
| Net Interest Income | 41,620 | 41,125 | 39,500 | 1.2% | 5.4% |
| Non-Interest Income | 15,271 | 11,162 | 10,791 | 36.8% | 41.5% |
| Operating Income | 56,890 | 52,287 | 50,291 | 8.8% | 13.1% |
| Interest on Deposits | 63,201 | 60,340 | 54,474 | 4.7% | 16.0% |
| Interest on Borrowings | 5,829 | 7,211 | 4,594 | -19.2% | 26.9% |
| Other Interest paid | 3,221 | 2,850 | 2,811 | 13.0% | 14.6% |
| Total Interest Expenses | 72,251 | 70,401 | 61,879 | 2.6% | 16.8% |
| Salary | 11,901 | 11,967 | 9,706 | -0.6% | 22.6% |
| Provisions for Employees | 2,906 | 3,499 | 9,221 | -16.9% | -68.5% |
| Staff Expenses | 14,807 | 15,466 | 18,926 | -4.3% | -21.8% |
| Overheads | 12,789 | 10,373 | 11,948 | 23.3% | 7.0% |
| Of which: Business Acquisition & Development Expenses | 1,491 | 1,061 | 1,509 | 40.5% | -1.2% |
| Operating Expenses | 27,596 | 25,839 | 30,874 | 6.8% | -10.6% |
| Total Expenses | 99,847 | 96,239 | 92,753 | 3.7% | 7.6% |
| Operating Profit | 29,294 | 26,449 | 19,417 | 10.8% | 50.9% |
| Total Provisions | 10,962 | 9,413 | 5,087 | 16.5% | 115.5% |
| Net Profit | 18,331 | 17,035 | 14,330 | 7.6% | 27.9% |
| NIM (Whole Bank) (%) | 3.14 | 3.22 | 3.29 | -2.5% | -4.6% |
| NIM (Domestic) (%) | 3.27 | 3.35 | 3.43 | -2.4% | -4.7% |
| Cost to Income Ratio (%) | 48.51 | 49.42 | 61.39 | -1.8% | -21.0% |
| Cost to Assets (%) | 1.76 | 1.67 | 2.17 | 5.4% | -18.9% |
| Ratios (Annualized) | Q2FY25 | Q1FY25 | Q2FY24 |
| ROA (%) | 1.17 | 1.10 | 1.01 |
| ROE (%) | 20.98 | ||
| Earning Per Share (₹) | 81.49 | 76.56 | 63.88 |
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
- Market Leadership
- Extensive Branch and ATM Network
- Ongoing Digital Transformation
- Strong Government Support and Diverse Product Portfolio
Weaknesses:
- High Debt Levels
- Constraints of Public Sector Operations
- Heavy Reliance on the Domestic Market
Opportunities:
- Growth in Digital Services
- Expansion in Rural Banking
- Increasing Demand for Retail Loans
- Supportive Government Initiatives
Threats:
- Fierce Market Competition
- Regulatory Compliance Risks
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
- Impact of Rising Interest Rates