IRFC Q2 Results: Revenue Rises 2%, Profit Up 4% YoY; Declares ₹0.8 Dividend per Share
Company Overview
Indian Railway Finance Corporation Limited (IRFC) was incorporated on December 12, 1986, as a Public Limited Company dedicated to supporting the financial needs of the Indian Railways. After receiving a Certificate of Commencement of Business on December 23, 1986, IRFC was classified as a Public Financial Institution in 1993 and later registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1998 as a non-banking financial institution. Over time, it evolved into a non-deposit accepting asset finance NBFC in 2008 and was subsequently reclassified as an NBFC-ND-IFC (Infrastructure Finance Company) by the RBI in 2010.
IRFC, under the administrative control of the Ministry of Railways (MoR), operates as the dedicated financing arm of the Indian Railways, securing funds from both domestic and international markets to finance its growth. Since inception, it has been crucial in funding rolling stock acquisitions and railway infrastructure projects for Indian Railways and related entities like Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) and IRCON.
The President of India, through the MoR, holds 86.36% of IRFC’s equity, with the remaining 13.64% owned by public shareholders, highlighting the company’s strategic importance. IRFC’s primary business is to borrow funds and finance assets that are leased to Indian Railways on long-term finance leases. It focuses on acquiring rolling stock assets—such as locomotives, coaches, wagons, containers, and cranes—and leasing infrastructure projects, thus ensuring steady financing for expansion and modernization. The leasing model typically spans 30 years, divided into a primary 15-year period where IRFC recovers the principal and borrowing costs, followed by a secondary 15-year period at a nominal lease rate.
In the 2020-21 fiscal year, IRFC financed a substantial 67.43% of Indian Railways’ capital outlay (Rs. 1,55,161 crore), contributing Rs. 1,04,369 crore to infrastructure needs, highlighting its pivotal role in India’s rail infrastructure. Notably, IRFC also supports initiatives like the Gati Shakti Multi-Modal Cargo Terminal (GCT) policy, launched in December 2021 to develop additional terminals for rail cargo, further solidifying its role in india’s logistics and transport infrastructure. Over three decades, IRFC has been instrumental in enabling capacity enhancement for the Indian Railways, helping the organization keep pace with India’s growing transportation demands.
Industry Outlook
India’s rail network is advancing at an unprecedented pace, positioning it to become the third-largest rail network globally in the next five years, with a projected 10% share of the global rail market. Two pivotal government initiatives are set to drive private investments: private passenger trains operated by private entities across the network and a comprehensive railway station redevelopment program.
These initiatives are anticipated to attract over US$ 7.5 billion in private investment in the coming five years. Under the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), Indian Railways has allocated more than ₹13.67 lakh crore for investment by 2025, accounting for 12% of the total planned infrastructure investment. The Draft National Rail Plan further envisions ₹38.22 lakh crore in capital expenditure for the rail sector by 2050. With the introduction of the semi-high-speed Vande Bharat trains, Indian Railways aims to operate 75 trains over 10-12 lakh kilometers by 2025-26.
The government’s focus on infrastructure is fueling railway development, with an ambitious plan to invest ₹50 lakh crore (US$ 715.41 billion) by 2030. This emphasis, coupled with favorable policy frameworks, is expected to encourage participation from both domestic and International private players, further boosting passenger and freight transport and supporting long-term sector growth.
Business Segments
Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) continues to focus on several key business segments that align with its role as the financial backbone of Indian Railways. These segments are as follows-
- Rolling Stock Financing: This is IRFC’s largest business segment, primarily dedicated to funding the procurement of rolling stock assets like locomotives, passenger coaches, and wagons. By supporting Indian Railways in addressing the growing transportation demand, IRFC plays a crucial role in capacity enhancement across the network.
- Railway Infrastructure Projects: IRFC finances essential infrastructure projects, including dedicated freight corridors, multi-modal logistics parks, and station redevelopment. These efforts align with the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) to strengthen logistics and connectivity nationwide, supporting economic and industrial growth.
- High-Speed Rail Corridors and Modernization: A critical area for IRFC is the funding of high-speed and semi-high-speed rail projects. The Vande Bharat trains and other initiatives aim to establish multiple high-speed corridors by FY26, significantly reducing travel time on key routes. IRFC ensures timely funding for these transformative projects.
- Energy and Green Projects: With sustainability as a priority, IRFC supports green energy initiatives within Indian Railways, including solar and wind power installations along rail networks. These projects align with the Indian Railways’ goal of achieving a net-zero carbon footprint by 2030, advancing India’s commitment to environmental sustainability.
- Joint Ventures and Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs): IRFC collaborates through joint ventures and SPVs with state entities and private players to enhance freight and passenger capabilities. These projects leverage public-private partnership (PPP) models to create backward and forward linkages within Indian Railways, boosting efficiency and innovation.
Through these key segments, IRFC strategically supports the modernization and expansion of Indian Railways, contributing significantly to national infrastructure goals and promoting a sustainable rail network.
Key Subsidiaries and Their Information
As of FY25, Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) continues to operate without any major subsidiaries directly associated with its core business operations. However, IRFC collaborates closely with various entities, particularly in public-private partnership (PPP) arrangements and special-purpose vehicles (SPVs), aimed at enhancing rail infrastructure projects and rolling stock for Indian Railways. These partnerships align IRFC with infrastructure development initiatives, especially as the government prioritizes rail network expansion and modernization across India.
Q2 FY25 Highlights
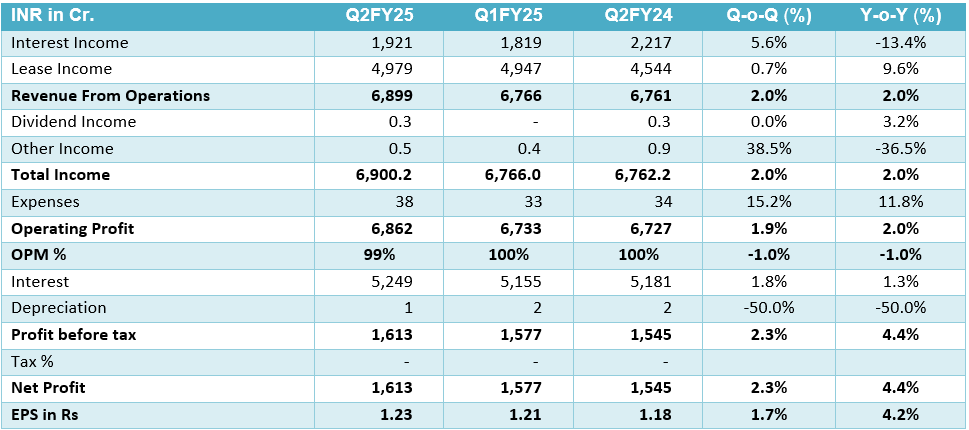
- Revenue from Operations has been ₹6,899 crore, marking a 2% YoY increase. Net Profit (PAT) of ₹1,612 crore, showing a 4% YoY growth from ₹1,544 crore in Q2 FY24.
- Operating Profit of ₹1,650.6 crore, reflecting a 4.5% YoY increase from ₹1,579.53 crore. Total Expenses stood at₹5,287.55 crore, reflecting a slight 1% rise compared to ₹5,217.60 crore in Q2 FY24.
- IRFC’s net worth increased to ₹51,464.12 crore in Q2 FY25, a significant rise from ₹46,883.22 crore in the same quarter of FY24, reflecting the company’s improved financial position. The debt-equity ratio stood at 7.83 in the September 2024 quarter, down from 8.67 in Q2 FY24, indicating a slight reduction in leverage and improved financial stability.
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) has set November 12, 2024, as the record date to determine the shareholders who are eligible for the interim dividend. This means that shareholders registered as of this date will be entitled to receive the interim dividend declared by the company.
- The IRFC Board has approved the financing of 20 Bogie Open Bottom Rapid (BOBR) rakes under the General-Purpose Wagon Investment Scheme (GPWIS) of the Ministry of Railways (MoR) to NTPC for up to ₹700 crore under a Finance Lease. IRFC has entered into Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) with RITES and IIFCL to form strategic collaborations aimed at enhancing its operational and financing capabilities for future railway projects.
Financial Summary
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
- Strategic alignment with Indian Railways
- Strong government backing
- Expanding asset portfolio
- Solid market presence
Weaknesses:
- High debt burden
- Limited revenue sources
- Sensitivity to operating margins
Opportunities:
- Infrastructure growth
- Private sector collaborations
- Adoption of new technology
- Green financing potential
Threats:
- Regulatory compliance demands
- Rising competition
- Economic and geopolitical risks
- Interest rate fluctuations