HDFC Bank Q2 Results: Net Profit Up 5.3% to ₹16,821 Crore; NII Rises 10% Year-Over-Year Amid Declining Asset Quality
Company Overview
HDFC Bank Limited (also known as HDFC) is an Indian banking and financial services company headquartered in Mumbai. It is India’s largest private sector bank by assets and the world’s tenth-largest bank by market capitalization. The company is India’s one of 3 systemically important banks with a 15% market share in the banking sector’s advances and a 37% market share in the private sector banks’ advances as of FY24. It is also the second-largest bank in India. The Bank has a distribution network of 8,851 branches and 21,163 ATMs across 4,081 cities.
Industry Outlook
Indian banks are witnessing a resurgence in credit demand, driven by growth across retail, MSME (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises), and corporate segments. Credit growth is expected to be 10-12% in FY25, fuelled by increased consumption, infrastructure spending, and recovery in sectors like real estate and manufacturing. NPAs expected to decline to around 4% in FY25. Enhanced risk management practices, improved loan recovery rates, and a healthier economic environment are contributing to better asset quality, which is likely to support profitability. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is focused on strengthening the banking sector through regulations around capital adequacy, governance, and digital banking frameworks.
Segmental Information
- Wholesale Banking: The Wholesale Banking Business of HDFC Bank serves a diverse clientele including Large Corporates, Multinational Corporations, Government, Public Sector Enterprises, Emerging Corporates and Business Banking/SMEs. Offering a wide array of financial products and services such as loans, deposits, payments, collections, tax solutions, trade finance, cash management solutions and corporate cards, etc. This business largely covers the rental discounting business as well as construction finance.
- Retail Banking: HDFC Bank’s Retail Business caters to a varied client base which includes Individuals, salaried professionals, small businesses like kirana stores, and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs). Among the offerings are Savings and Current Accounts, various loan options for personal and business needs, Credit and Debit Cards, Digital Wallets, Insurance and Investment Products and Remittance Services.
- Treasury: The Treasury department is responsible for managing the Bank’s liquidity requirements, as well as handling its investments in securities and other market instruments. It manages the balance sheet’s liquidity and interest rate risks and ensures compliance with statutory reserve requirements. It also manages the treasury needs of customers and earns a fee income generated from transactions customers undertake with your Bank, while managing their foreign exchange and interest rate risks.
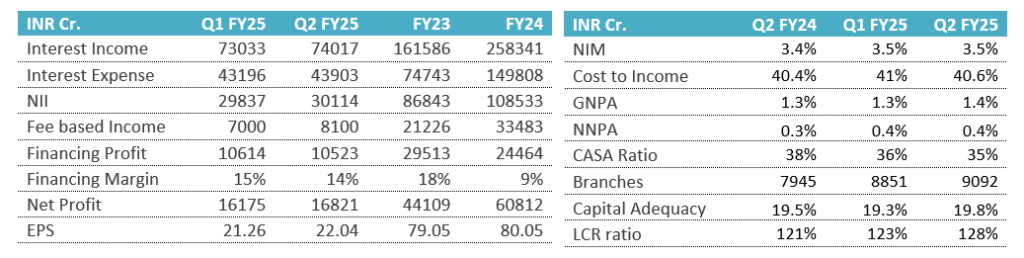
Quarterly Highlights
- Revenue for Q2 FY25 is Rs 74,017 compared to Rs 67,698 crore in Q2 FY24.
- Financing profit of Rs 10523 crore in this quarter, with the margin of 14%.
- Net Profit is Rs 16821 crore in Q2 up from Rs 15,976 crore in Q2 FY24.
Operational Highlights
- Average Deposits in Q2 were Rs 23,540 bn up by 15.5% YoY, growth in Advances under management is 10.2% YoY to Rs 25,639 bn. The fee income is around Rs 8000 crore for Q2.
- Retail/Wholesale deposits are 84% & 16% respectively for Q2 FY25. And the CASA deposits are Rs 2754 bn for Current Accounts, Rs 6081 bn for Savings Accounts and the CASA ratio is 35% for Q2 FY25.
- Branch network in Q2 is of 9092 branches, of which Semi-Urban has highest branches accounting for 34%.
- The Net revenue mix is 72% for Net Interest Income and 28% for Non-Interest Income, and this proportion has steady.
- The Yield on Assets are 8.3% and cost of funds are 4.9%. Their difference shows us the earnings of bank through lending it to retail. Lower the cost, higher the profit margin in lending.
Financial Summary and Key Ratios
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
- Strong asset quality
- Extensive branch network
- Market leadership position
Weaknesses:
- High reliance on retail loans
- Elevated valuations
- Regulatory pressures
Opportunities:
- Growth potential in SME and MSME lending
- Expansion of wealth management services
- Increasing financial inclusion
Threats:
- Intense competition
- Risk of economic slowdown
- Cybersecurity threats

