IRFC Share Price Crashes 50% from Peak, Hits 52-Week Low– Will It Drop to ₹100?
Business and Industry Overview:
Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) is the finance company of Indian Railways. It was started in 1986 to arrange money for railway projects. The company helps Indian Railways buy trains, coaches, and wagons. It also gives money for building railway infrastructure.
IRFC borrows money from banks, bonds, and other sources at low-interest rates. It then lends this money to Indian Railways at a small profit. This helps railways grow without money problems.
IRFC has strong finances and earns steady profits. Since it is owned by the Indian government, it is a safe company to invest in. It also pays regular dividends to its investors.
The Ministry of Railways controls IRFC, and the Government of India owns most of its shares. IRFC supports high-speed rail, electrification, and railway expansion. Its growth depends on government spending on railways. The company plays a big role in modernizing Indian Railways while keeping costs under control.
Since IRFC is a public sector company, it is controlled by the Ministry of Railways. The Government of India holds the majority stake, making it a safe investment option for long-term investors. The government’s continued focus on railway modernization and expansion ensures that IRFC will remain financially strong.
Potentials:
The Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) has a strong future. The government is improving railways with better trains, faster travel, and new tracks. IRFC will raise more money through bonds, loans, and foreign investments. It will also finance big railway projects like high-speed trains, freight corridors, and logistics parks. IRFC helps Indian Railways buy new trains, coaches, and wagons. It is also working on solar and wind energy to make railways eco-friendly. The company wants to offer better services to investors and lenders. It is also training employees for better management. Since 2011-12, IRFC has funded many railway projects. It will continue supporting railway growth in the future. With government support and steady profits, IRFC will help Indian Railways grow and improve.
Latest Stock News:
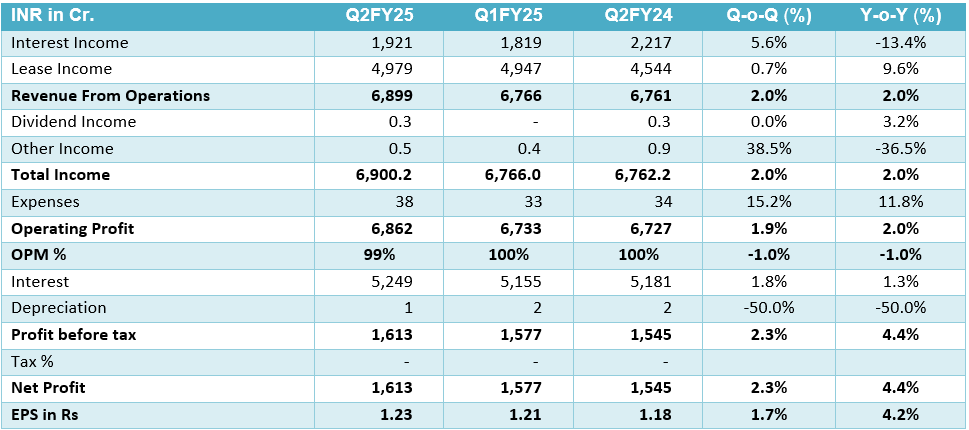
Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) has seen a sharp decline in its stock price, dropping nearly 50% from its peak of ₹229 over the past six months, with the latest close at ₹119.98 on February 14, 2025. The stock is trading below moving averages, indicating a bearish trend, with an upper circuit limit of ₹132.39 and a lower circuit limit of ₹108.32. The decline is due to sector challenges, reduced funding requests from Indian Railways, and IRFC’s shift towards new lending areas like logistics and urban mobility. Despite having a strong financial base with a market capitalization of ₹1,46,916 crore, experts believe the stock may fall further if it breaks the ₹96 support level. While some analysts see resistance at ₹130-₹132, Moneycontrol experts recommend selling IRFC shares as it remains in a negative trend with oversold technical indicators. Given the heavy selling pressure on mid and small-cap stocks, investors are advised to exit for now and reconsider entry once the stock stabilises. Always consult a financial expert before making investment decisions.
Analyst Insights:
- Market capitalisation: 55,744 Cr.
- Current Price: ₹ 343
- 52-Week High/Low: ₹ 768 / 341
- P/E Ratio: 7.56
- Dividend Yield:3.06 %
- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE): 17.7 %
- Return on Equity (ROE): 18.0 %
Oil India Ltd (OIL) is currently trading at ₹343, near its 52-week low of ₹341, with a market capitalization of ₹55,744 Cr. It has a low P/E ratio of 7.56, indicating undervaluation, and offers a stable dividend yield of 3.06% with a payout ratio of 30.8%. The company shows strong profitability with an ROCE of 17.7% and ROE of 18.0%, making it attractive for long-term investors. However, concerns include extremely high debtor days (3,557 days), a low interest coverage ratio, and significant debt, which raises financial risks. Additionally, possible capitalization of interest costs needs closer examination. The stock is in a downward trend, indicating weak sentiment in the short term. Given the financial risks and technical weakness, a Sell recommendation is advised for the short term, while long-term investors may consider holding if the company improves its cash flow and debt position. Existing investors should monitor receivables and debt closely before making further commitments.